7 FHIR - DataType
7.1 Primitive Types Overview
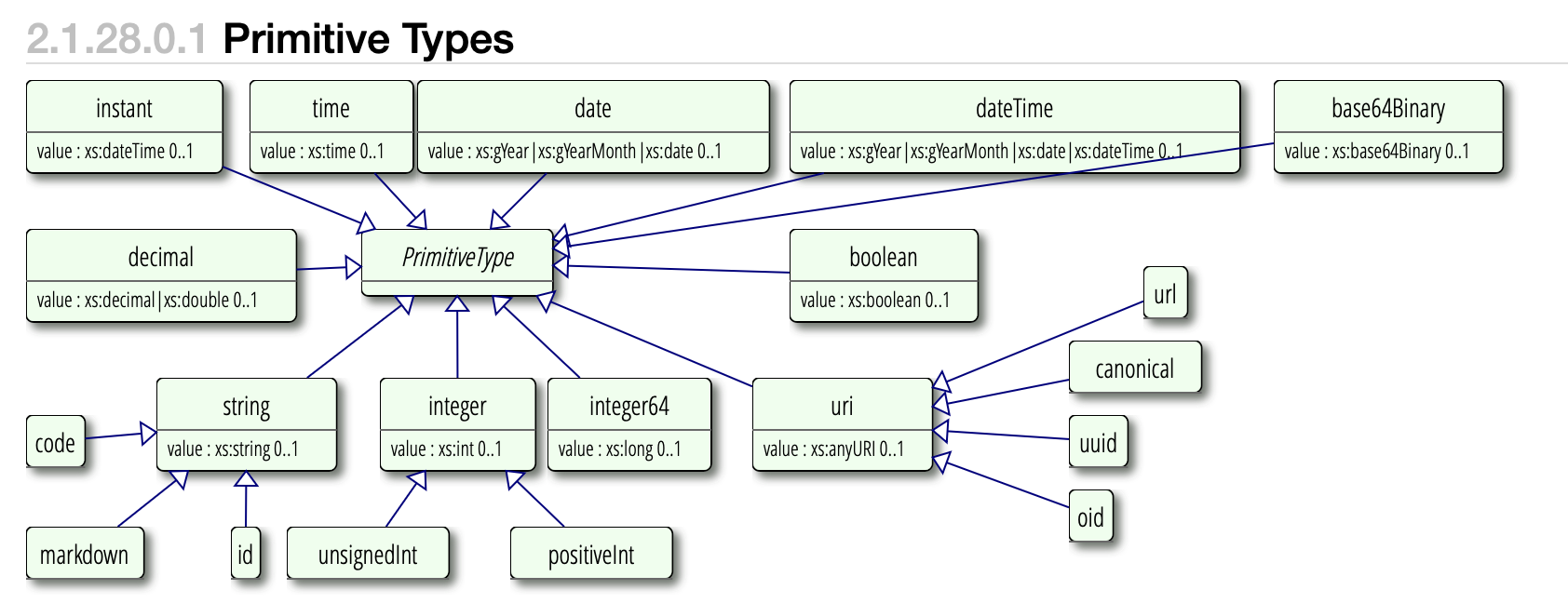
Based on the diagram, FHIR primitive types form the foundation for all data representation. Let me break down each type:
7.1.1 String-Based Types
7.1.1.1 string
- Meaning: General-purpose text data with Unicode support
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"patientName": "John Smith",
"radiologistNote": "Patient cooperative during exam"
}7.1.1.2 code
- Meaning: A string constrained to a specific set of values defined by a code system
- JSON Representation: JSON string (but must match predefined values)
- Examples:
{
"status": "final", // DiagnosticReport status
"modality": "CT", // Imaging modality
"bodyPart": "chest" // Anatomical region
}7.1.1.3 markdown
- Meaning: String that may contain markdown formatting
- JSON Representation: JSON string with markdown syntax
- Examples:
{
"reportText": "**FINDINGS:**\n\n1. No acute findings\n2. *Minimal* pleural effusion",
"instructions": "Patient should **fast** for 4 hours before contrast CT"
}7.1.1.4 id
- Meaning: Logical identifier for resources (letters, digits, hyphens, periods)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"id": "imaging-study-001",
"patientId": "patient-12345",
"reportId": "rad-report-2024-001"
}7.1.2 Numeric Types
7.1.2.1 decimal
- Meaning: Rational numbers with arbitrary precision (preserves trailing zeros)
- JSON Representation: JSON number or string
- Examples:
{
"lesionSize": 12.50, // Preserves precision for measurements
"contrastVolume": 100.0, // ML of contrast agent
"tubeVoltage": 120.0 // kVp setting
}7.1.2.2 integer
- Meaning: Signed 32-bit integers (-2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647)
- JSON Representation: JSON number
- Examples:
{
"numberOfSeries": 4,
"numberOfInstances": 256,
"studyAge": 45
}7.1.2.3 integer64
- Meaning: Signed 64-bit integers for large values
- JSON Representation: JSON string (to preserve precision)
- Examples:
{
"dicomInstanceSize": "2147483648", // File size in bytes
"pixelDataLength": "134217728" // Large pixel data
}7.1.2.4 unsignedInt
- Meaning: Non-negative 32-bit integers (0 to 2,147,483,647)
- JSON Representation: JSON number
- Examples:
{
"seriesNumber": 1,
"instanceNumber": 45,
"repetitionTime": 500 // MRI TR in milliseconds
}7.1.2.5 positiveInt
- Meaning: Positive integers (1 and above)
- JSON Representation: JSON number
- Examples:
{
"numberOfSlices": 128,
"matrixSize": 512,
"echoTime": 25 // MRI TE in milliseconds
}7.1.3 Date and Time Types
7.1.3.1 instant
- Meaning: Precise timestamp with timezone (YYYY-MM-DDTHH:mm:ss.sss+zz:zz)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"acquisitionDateTime": "2024-01-15T14:30:15.123Z",
"reportSignedAt": "2024-01-15T16:45:00.000-05:00"
}7.1.3.2 dateTime
- Meaning: Date and optionally time (partial precision allowed)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"studyDate": "2024-01-15T14:30:00Z",
"birthDateTime": "1980-03-15",
"symptomOnset": "2024-01" // Year and month only
}7.1.3.3 date
- Meaning: Date without time (YYYY, YYYY-MM, or YYYY-MM-DD)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"birthDate": "1980-03-15",
"studyDate": "2024-01-15",
"priorExamDate": "2023-12"
}7.1.3.4 time
- Meaning: Time of day (HH:mm:ss or HH:mm:ss.sss)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"scheduledTime": "14:30:00",
"acquisitionTime": "14:32:15.123"
}7.1.4 Other Important Types
7.1.4.1 boolean
- Meaning: True or false values
- JSON Representation: JSON boolean
- Examples:
{
"isPregnant": false,
"contrastUsed": true,
"isUrgent": true
}7.1.4.2 uri
- Meaning: Uniform Resource Identifier
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"profileUrl": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/Patient",
"codingSystem": "http://snomed.info/sct"
}7.1.4.3 url (subset of uri)
- Meaning: Uniform Resource Locator (accessible web address)
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"pacsUrl": "https://pacs.hospital.com/study/123",
"dicomWebUrl": "https://dicomweb.example.com/studies/1.2.3.4"
}7.1.4.4 canonical (subset of uri)
- Meaning: URI that refers to a FHIR resource with canonical URLs
- JSON Representation: JSON string
- Examples:
{
"profile": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/ImagingStudy",
"valueSet": "http://hl7.org/fhir/ValueSet/body-site"
}7.1.4.5 uuid (subset of uri)
- Meaning: Universally Unique Identifier
- JSON Representation: JSON string (urn:uuid: prefix)
- Examples:
{
"messageId": "urn:uuid:550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
"studyInstanceUID": "urn:uuid:1.2.840.113619.2.176.2025.1.1.1"
}7.1.4.6 oid (subset of uri)
- Meaning: Object Identifier (hierarchical dotted notation)
- JSON Representation: JSON string (urn:oid: prefix)
- Examples:
{
"institutionOID": "urn:oid:1.2.840.113619.2.176",
"dicomUID": "urn:oid:1.2.840.10008.1.2.1"
}7.1.4.7 base64Binary
- Meaning: Binary data encoded as base64 string
- JSON Representation: JSON string (base64 encoded)
- Examples:
{
"thumbnailImage": "iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAAAEAAAABCAYAAAAfFcSJAAAADUlEQVR42mP8/5+hHgAHggJ/PchI7wAAAABJRU5ErkJggg==",
"digitalSignature": "SGVsbG8gV29ybGQ="
}7.1.5 Radiology-Specific Usage Examples
{
"resourceType": "ImagingStudy",
"id": "ct-chest-001", // id
"status": "available", // code
"started": "2024-01-15T14:30:00Z", // dateTime
"numberOfSeries": 3, // unsignedInt
"numberOfInstances": 128, // unsignedInt
"description": "CT Chest with contrast", // string
"procedureCode": {
"system": "http://loinc.org", // uri
"code": "24627-2" // code
},
"subject": {
"reference": "Patient/patient-123" // string (but reference format)
}
}7.2 URI, URL, Canonical, UUID
These types form a hierarchy where each is a subset of the previous:
- uri (most general)
- url (subset of uri)
- canonical (subset of uri)
- uuid (subset of uri)
7.2.1 1. uri (Uniform Resource Identifier)
Definition: The most general identifier that can name or locate any resource. It includes both URLs (locators) and URNs (names).
Purpose: Generic identifier for any kind of resource, concept, or entity.
Format: Any valid URI scheme
Examples:
{
"codeSystem": "http://snomed.info/sct",
"namespace": "urn:ietf:rfc:3986",
"telephone": "tel:+1-555-123-4567",
"email": "mailto:radiologist@hospital.com",
"fhirProfile": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/Patient"
}7.2.2 2. url (Uniform Resource Locator)
Definition: A URI that provides the means to locate and access a resource over a network (typically HTTP/HTTPS).
Purpose: Points to an actual, accessible web resource.
Format: Must be a valid URL that can be resolved/accessed
Examples:
{
"pacsEndpoint": "https://pacs.hospital.com/wado-rs",
"dicomWebStudy": "https://dicomweb.example.com/studies/1.2.3.4.5",
"imagingReportPdf": "https://reports.radiology.com/reports/12345.pdf",
"terminologyService": "https://tx.fhir.org/r4",
"patientPortal": "https://portal.hospital.com/patient/123"
}7.2.3 3. canonical (Canonical URI)
Definition: A URI that refers to a FHIR resource that has a canonical URL (like StructureDefinitions, ValueSets, CodeSystems).
Purpose: References FHIR conformance resources and ensures version-independent referencing.
Format: URI that identifies a FHIR canonical resource, may include version
Examples:
{
// FHIR Structure Definitions
"profile": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/ImagingStudy",
"patientProfile": "http://hl7.org/fhir/us/core/StructureDefinition/us-core-patient",
// Value Sets
"bodyPositionValueSet": "http://hl7.org/fhir/ValueSet/body-site",
"modalityValueSet": "http://dicom.nema.org/medical/dicom/current/output/chtml/part16/sect_CID_29.html",
// Code Systems
"loincSystem": "http://hl7.org/fhir/CodeSystem/loinc",
"snomedSystem": "http://hl7.org/fhir/CodeSystem/snomed-ct",
// Implementation Guides
"radiologyIG": "http://hl7.org/fhir/us/breast-radiology/ImplementationGuide/hl7.fhir.us.breast-radiology",
// With version
"profileWithVersion": "http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/Patient|5.0.0"
}7.2.4 4. uuid (Universally Unique Identifier)
Definition: A 128-bit identifier that is unique across time and space, formatted as a URN with “urn:uuid:” prefix.
Purpose: Provides globally unique identifiers without central coordination.
Format: urn:uuid: followed by 8-4-4-4-12 hexadecimal digits
Examples:
{
// Message identifiers
"messageId": "urn:uuid:550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000",
// DICOM Study Instance UIDs (when represented as UUID)
"studyInstanceUID": "urn:uuid:6ba7b810-9dad-11d1-80b4-00c04fd430c8",
// Transaction/Bundle identifiers
"bundleId": "urn:uuid:3fa85f64-5717-4562-b3fc-2c963f66afa6",
// Temporary resource identifiers
"tempPatientId": "urn:uuid:12345678-90ab-cdef-1234-567890abcdef",
// Document identifiers
"documentId": "urn:uuid:a54d6aa5-d40d-43f9-88c5-b4633d873bdd"
}7.2.5 Practical Radiology Examples
7.2.5.1 Complete ImagingStudy Resource Example
{
"resourceType": "ImagingStudy",
"id": "ct-chest-001",
// uri - general identifier for code system
"identifier": [{
"system": "http://hospital.com/imaging-studies", // uri
"value": "STUDY-001"
}],
// url - actual accessible endpoint
"endpoint": [{
"reference": "https://pacs.hospital.com/wado-rs/studies/1.2.3.4" // url
}],
// canonical - reference to FHIR profile
"meta": {
"profile": ["http://hl7.org/fhir/StructureDefinition/ImagingStudy"] // canonical
},
// uuid - unique identifier for this specific study
"identifier": [{
"system": "urn:dicom:uid",
"value": "urn:uuid:6ba7b810-9dad-11d1-80b4-00c04fd430c8" // uuid
}]
}7.2.5.2 DiagnosticReport Example
{
"resourceType": "DiagnosticReport",
"id": "radiology-report-001",
// canonical - reference to diagnostic report profile
"meta": {
"profile": ["http://hl7.org/fhir/us/core/StructureDefinition/us-core-diagnosticreport-note"] // canonical
},
// uri - code system identifier
"category": [{
"coding": [{
"system": "http://terminology.hl7.org/CodeSystem/v2-0074", // uri
"code": "RAD"
}]
}],
// url - link to actual report document
"presentedForm": [{
"contentType": "application/pdf",
"url": "https://reports.hospital.com/rad-reports/001.pdf" // url
}],
// uuid - unique identifier for report
"identifier": [{
"system": "urn:ietf:rfc:3986",
"value": "urn:uuid:550e8400-e29b-41d4-a716-446655440000" // uuid
}]
}7.2.6 Key Differences Summary
| Type | Purpose | Accessibility | Example Domain |
|---|---|---|---|
| uri | General identifier | May or may not be accessible | Any identifier system |
| url | Locatable resource | Must be network accessible | Web endpoints, APIs |
| canonical | FHIR resource reference | May be accessible, version-aware | FHIR profiles, value sets |
| uuid | Unique identifier | Not accessible (just identifier) | Temporary IDs, message IDs |
7.2.7 When to Use Each
- uri: When you need to identify a code system, namespace, or any resource
- url: When pointing to actual web resources (PACS endpoints, documents, APIs)
- canonical: When referencing FHIR conformance resources (profiles, value sets)
- uuid: When you need guaranteed unique identifiers without central coordination
Understanding these distinctions is crucial for proper FHIR implementation in radiology systems, ensuring correct data exchange and interoperability.